备份
命令行下具体用法如下:
mysqldump -u用戶名 -p密码 -d 数据库名 表名 > 脚本名;
导出整个数据库结构和数据mysqldump -h localhost -uroot -p123456 database > dump.sql
导出单个数据表结构和数据mysqldump -h localhost -uroot -p123456 database table > dump.sql
导出整个数据库结构(不包含数据)mysqldump -h localhost -uroot -p123456 -d database > dump.sql
导出单个数据表结构(不包含数据)mysqldump -h localhost -uroot -p123456 -d database table > dump.sql
数据还原
1、还原使用mysqldump命令备份的数据库的语法如下:mysql -u root -p [dbname] < backup.sq
示例:mysql -u root -p < C:\backup.sql
JUC源码学习之AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
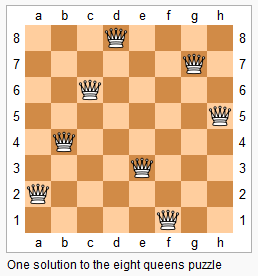
N皇后问题
1 | import java.util.ArrayList; |
Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
Given a string containing digits from 2-9 inclusive, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent.
A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below. Note that 1 does not map to any letters.

1 | import java.util.ArrayList; |
Generate Parentheses
Given n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
For example, given n = 3, a solution set is:
1 | [ |
1 | class Solution { |
Sudoku Solver
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
Each of the the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
Empty cells are indicated by the character ‘.’.
1 | /* |
Combination Sum

相关问题:Combination Sum II
1 |
|
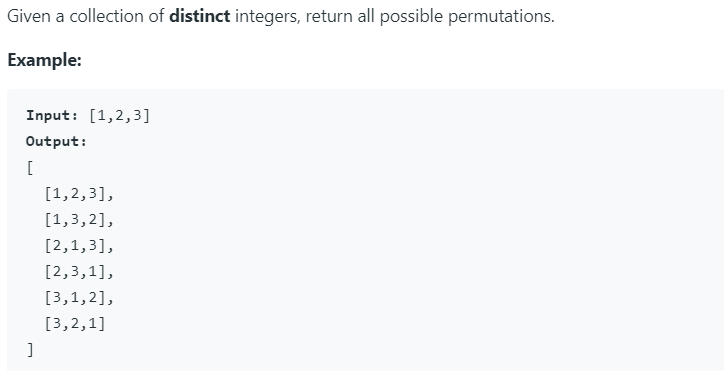
Permutations
相关问题:Permutations II
1 | class Solution { |
Permutation Sequence

1 | class Solution { |
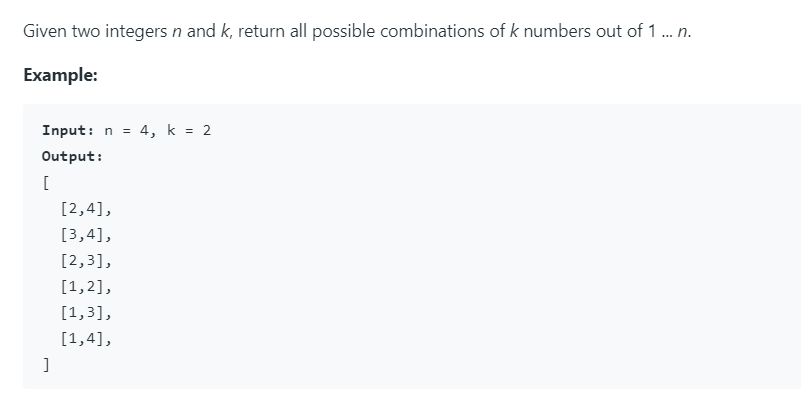
Combinations
1 | class Solution { |
大概一年多前,用过Netty做局域网内自动组网,但是当时的主要代码不是我写的,并且时间过了很久,忘得差不多了,然而发现Netty确实是一个很有意思的框架,值得去深入研究、学习。本文的例子,之前也看过、写过,在各种介绍Netty的书籍中都有看到,并且Netty的官方文档也有这样的例子。
EchoServer
Netty官方Echo例子,其实在源码中也有该例子。
EchoServer
1 | import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; |
EchoServerHandler
1 | import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; |
EchoClient
1 | public class EchoClient { |
EchoClientHandler
1 | import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; |
TimeServer
这个例子主要来自《Netty权威指南》,包括后面的粘包和拆包的例子都是基于此demo。
TimeServer
1 | public class TimeServer { |
1 | import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; |
TimeClient
1 | import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; |
TimeClientHandler
1 | import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; |
这里的代码是已经处理好了粘包/拆包问题,如果要看粘包/拆包的现象,只需要将LineBasedFrameDecoder和StringDecoder不加入到pipeline中即可。
参考:
https://netty.io/wiki/index.html
https://netty.io/wiki/user-guide-for-4.x.html




